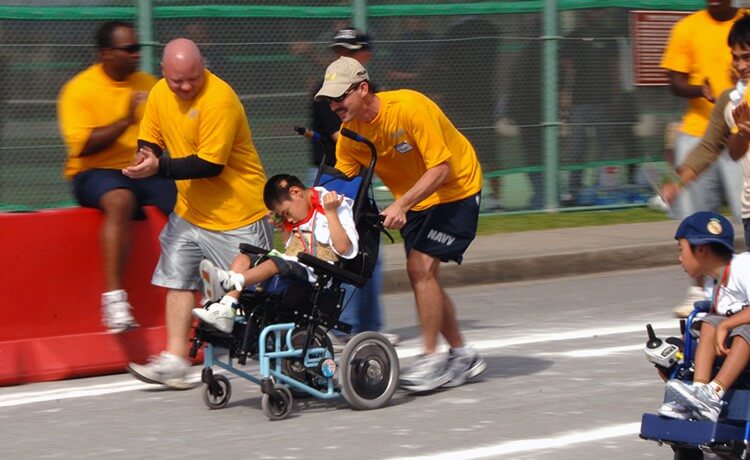
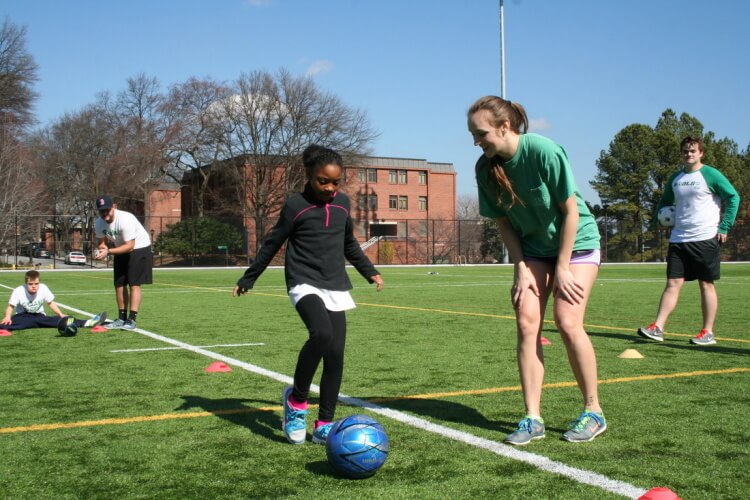
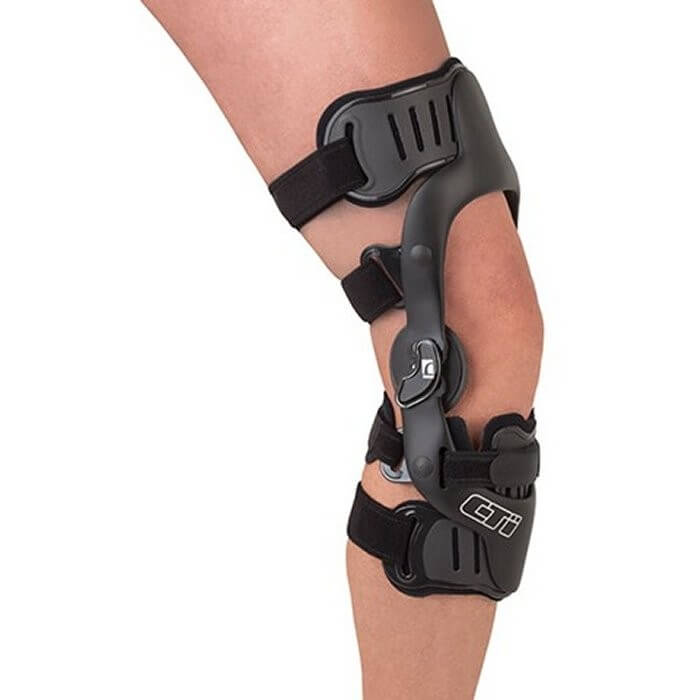
Bracing and orthotic management for children with disabilities is often overlooked in physical education. Orthotics may be defined as custom-made devices that are fabricated to address musculoskeletal deformities, deficits, or discrepancies, while attempting to increase function or regain mobility of a specific musculoskeletal structure.
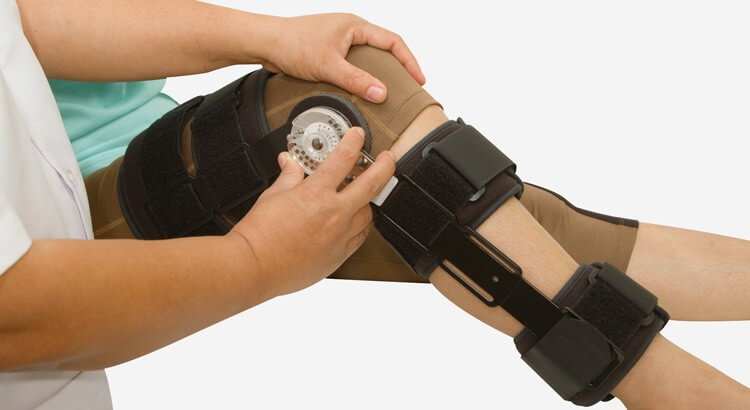
Orthotic wearing schedules, maintenance, and compliance are among some of the most important components leading to successful orthotic interventions or treatment plans. Physicians, orthotists, and therapists work diligently to select the most appropriate orthotic device for a child while considering his or her diagnosis, physical limitations, level of cognition, gait abnormalities, range of motion (ROM), skin sensitivities, and environmental factors. Because children wearing orthotic devices spend most of their time in school settings, it is important for adapted physical educators to understand the basic components of orthotic management in order to meet treatment goals, increase physical function, and most importantly to ensure the safety of the child.
Wearing Schedules
Typically, orthotic braces are prescribed to maintain alignment, prevent further deformity, and facilitate independence during functional activities. Orthotists and therapists generally instruct orthotic patients to wear the device during all physical activities, and recommend disuse of the orthosis during several activities of daily living such as bathing and sleeping. Adapted physical educators should keep the following factors in mind when working with special needs students who wear custom-made orthotics: